Diabetes Mellitus is a metabolic disorder of high blood glucose levels in the blood stream due to the defects in secretion or action of insulin (type of hormone) released from the pancreas. It is also called “sweet urine disorder” due to the elevated levels of glucose spilling from the blood stream into the urine.
Types of Diabetes
Type 1
diabetes is called insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) or juvenile onset diabetes mellitus where the pancreas is incapable of making insulin. IDDM usually occurs in people before 30 years of age, however, older patients may also suffer from a similar condition known as latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA).
Type 2
diabetes is called non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) or adult onset diabetes mellitus (AODM). Here, the patients can still produce insulin, but in a defective pattern which means over or under production. Type 2 diabetes occurs mostly in individuals over 30 years of age, but may affect the age group below as a direct result of poor eating habits, higher body weight, and lack of exercise.
“Secondary” diabetes arises due to other medical conditions like the destruction of the pancreatic tissue, chronic pancreatitis trauma, or surgical removal of the pancreas. Diabetes can also result from other hormonal disturbances, such as excessive growth hormone production (acromegaly) and Cushing’s syndrome.
Physical symptoms
Increased urine output
Excessive thirst with dry mouth
Unusually high appetite
Excessive weight loss or gainF
atigue, nausea, vomiting
Prone to bladder, skin and vaginal infections
Blurred vision, lethargy
Tingling or numbness in the hands, legs or feet
Cause of Type 1 Diabetes
People with Type 1 diabetes have an abnormal immune system response where it attacks itself.
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
High blood pressure | High blood triglyceride (fat) levels | Gestational diabetes or giving birth to a baby weighing more than nine pounds | High-fat diet | High alcohol intake | Sedentary lifestyle | Obesity
Ethnicity, particularly when a close relative has had Type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes: certain groups, such as African Americans, Native Americans, Hispanic Americans, and Japanese Americans have a greater risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Aging: Increasing age is a significant risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. Risk begins to rise significantly at about 45 years, and rises considerably after 65 years of age.
Home remedies for Diabetes (Type 2)
Amla Juice/Amalaki Juice or Powder: Prepare a fine powder of dry amalaki. Put this powder in water and let it stand for some time. Then filter the solution and squeeze lemon juice into it. Take this early in the morning. It is very beneficial in controlling diabetes. You may alternately also drink two ounces of Amalaki juice every day by diluting it with two ounces of water.
Curry leaves: Curry leaves also control diabetes. Chew eight to ten young curry leaves on an empty stomach. This will be very effective in bringing the sugar levels in urine and blood to normal.
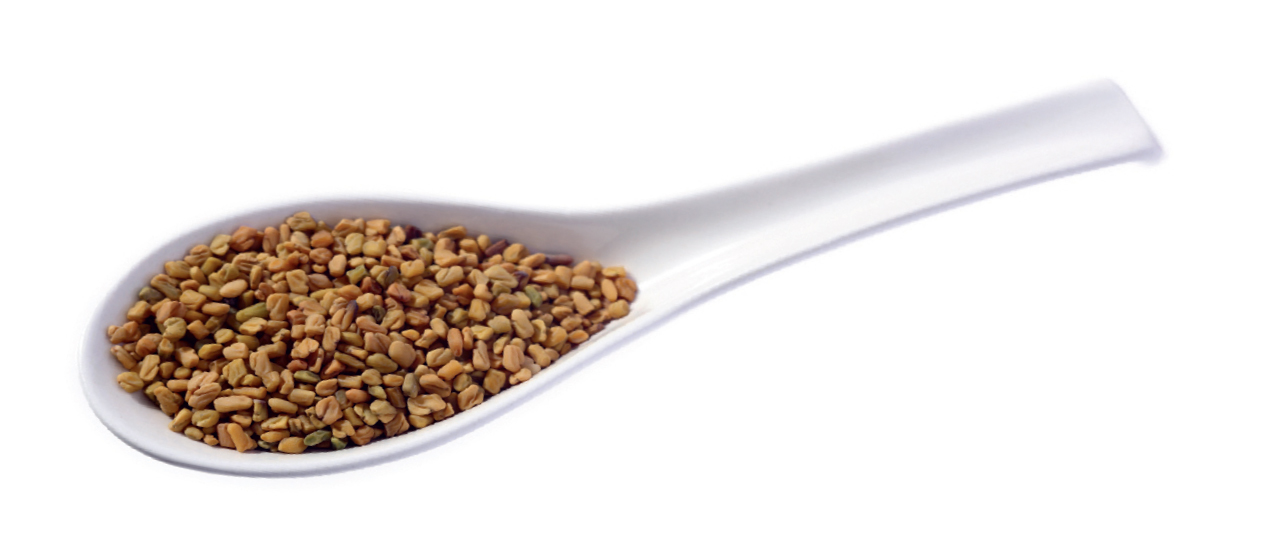
Fenugreek: It can suppress the excretion of sugar through urine. Fenugreek seeds are commonly used in lowering sugar levels. Soak one teaspoon of seeds in a glass of water and leave it overnight. In the morning, drink the water and eat the soaked seeds.
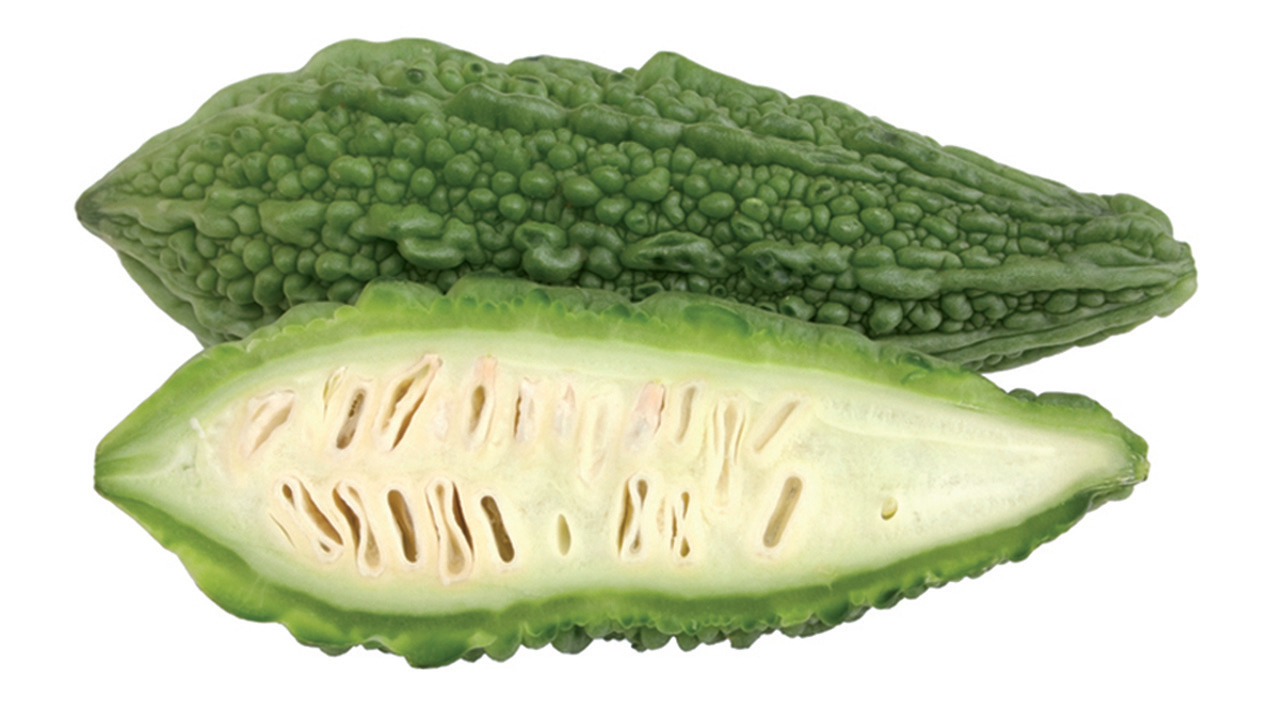
Juice: Juice of Bitter melon or Bitter gourd, Rose apple, or two tender leaves of Bilva and Neem may be taken on an empty stomach daily.
Copper Charged Water: Put one cup of water into a copper vessel at night, and drink the water in the morning on an empty stomach.

Aloe Vera and Turmeric: Turmeric with Aloe Vera gel (one to three grams) is best used during the early stages of diabetes for regulating pancreas and liver functions.
Cilantro leaves: Take five to seven strands of cilantro and boil them in three cups of water. Allow the mixture to boil for ten minutes or until it reduces to half the quantity. Drink it two times a day for ten days and keep a regular tab on the blood sugar levels by lab tests done every ten days.
Ayurveda: Regular intake of herbs like Shilajit, Gudmar Turmeric, Neem, Amalaki, Guggul and Arjuna can be very beneficial under a certified Ayurvedic doctor.

Aromatherapy: Massage the whole body with the following essential oil blend: Eucalyptus – 4%, Geranium – 4%, Juniper – 4% and Vegetable Oil base – 88%.
Additional tips to prevent Diabetes
- Avoid eating starchy foods (white bread, rice, potatoes and sweet, sugary foods) as they are not easily digestible.
- Avoid oily foods.
- Avoid coffee, sugar, refined flour and alcohol.
- Avoid very heavy lunches and dinners. In fact, eat regular and small meals every two hours.
- Combat the existing stress in your life through yoga, meditation and breathing.
- Avoid eating stale and junk food.
- Avoid late nights and irregular food and sleep patterns.
- Avoid a sedentary lifestyle and introduce regular exercise as part of your daily routine.
Disclaimer: If you are experiencing any or several of the symptoms, you should talk to your doctor about whether you have diabetes. You must verify with your physician before applying this article’s suggestions to your individual situation.
 Indu Arora, Ayurveda and Yoga Therapist considers herself a student for lifetime. She has been sharing about Yoga philosophy, Yoga Therapy and Ayurveda since 1999. She is inspired by and taught under Kriya Yoga, Himalayan Yoga, Kashmir Shivaism and Sivananda Yoga lineages. She has studied both Yoga and Ayurveda in a traditional Guru paramapara setting. Her teaching style is rooted in empowering and inspiring students to awaken the inner Guru. Her core philosophy is, ‘Nothing has the greatest power to heal, but Self!” www.yogsadhna.com
Indu Arora, Ayurveda and Yoga Therapist considers herself a student for lifetime. She has been sharing about Yoga philosophy, Yoga Therapy and Ayurveda since 1999. She is inspired by and taught under Kriya Yoga, Himalayan Yoga, Kashmir Shivaism and Sivananda Yoga lineages. She has studied both Yoga and Ayurveda in a traditional Guru paramapara setting. Her teaching style is rooted in empowering and inspiring students to awaken the inner Guru. Her core philosophy is, ‘Nothing has the greatest power to heal, but Self!” www.yogsadhna.com




